
(redirected from Positive ions)
Also found in: Dictionary, Thesaurus, Encyclopedia.
Ions charged with negative electricity (anions) travel toward a positive pole (anode); those charged with positive electricity (cations) travel toward a negative pole (cathode). Ions may exist in solid, liquid, or gaseous environments, although those in liquid (electrolytes) are more common and familiar. Positive ions are typically metals or act like metals. Many common materials contain these ions. Mercury is found in thermometers, for instance, and aluminum is a metal that is found in a surprising amount of things. It's even an ingredient in baking soda and in certain other food products!
Related to Positive ions: Negative ions
ion
[
i´onAn ion (/ ˈ aɪ ɒ n,-ən /) is a particle, atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of the electron is considered negative by convention. The negative charge of an ion is equal and opposite to charged proton(s) considered positive by convention.
]
an atom or group of atoms having a positive (cation) or negative (anion) electric charge by virtue of having gained or lost an electron; substances forming ions are called electrolytes. adj., adj ion´ic.
dipolar ion an ion that has both positive and negative regions of charge.
hydrogen ion the positively charged hydrogen atom (H+), which is the positive ion of all acids. See also hydrogen ion concentration.
hydroxyl ion the negatively charged group, OH−, present to excess in alkaline solutions.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
i·on
(
ī'onPositive Ions Effect On Body
),
An atom or group of atoms carrying an electric charge by virtue of having gained or lost one or more electrons. Ions charged with negative electricity (anions) travel toward a positive pole (anode); those charged with positive electricity (cations) travel toward a negative pole (cathode). Ions may exist in solid, liquid, or gaseous environments, although those in liquid (electrolytes) are more common and familiar.
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
i·on
(
ī'on)
An atom or group of atoms carrying an electric charge by virtue of having gained or lost one or more electrons. Ions charged with negative electricity (anions) travel toward a positive pole (anode); those charged with positive electricity (cations) travel toward a negative pole (cathode). Ions may exist in solid, liquid, or gaseous environments, although those in liquid (electrolytes) are more common and familiar.
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
ion
An electrically charged atom, group of atoms, or molecule. A positive ion is an atom that has lost an electron; a negatively charged ion is one that has gained an electron. See also IONIZATION.
Collins Dictionary of Medicine © Robert M. Youngson 2004, 2005
ion
an atom that carries a charge due to loss or gain of electrons.
Collins Dictionary of Biology, 3rd ed. © W. G. Hale, V. A. Saunders, J. P. Margham 2005
Ion
An atom or group of atoms that acquires an electrical charge by the gain or loss of electrons.
Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. Copyright 2008 The Gale Group, Inc. All rights reserved.
ion
(
ī'on)
An atom or group of atoms carrying an electric charge by virtue of having gained or lost one or more electrons. Ions charged with negative electricity (anions) travel toward a positive pole (anode); those charged with positive electricity (cations) travel toward a negative pole (cathode). Ions may exist in solid, liquid, or gaseous environments, although those in liquid (electrolytes) are more common and familiar.
Medical Dictionary for the Dental Professions © Farlex 2012
Want to thank TFD for its existence? Tell a friend about us, add a link to this page, or visit the webmaster's page for free fun content.

Link to this page:
Also found in: Dictionary, Thesaurus, Medical.
positive ion
[
′päz·əd·iv ′ī‚än] (chemistry)
An atom or group of atoms which by loss of one or more electrons has acquired a positive electric charge; occurs on ionization of chemical compounds as H+from ionization of hydrochloric acid, HCl.
McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Scientific & Technical Terms, 6E, Copyright © 2003 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
ion
(1) (
IDL
On the
Net) See IDL.
(2) (ION) An NVIDIA graphics platform typically used in Atom-based netbooks. See Intel Atom.
(3) An ion is an atom with fewer or greater electrons than normal as a result of radiation or chemical reaction. A positive ion, called a 'cation' (pronounced '
cat-eye-en'), has one or more electrons stripped out, which means it has fewer electrons in its electron shells than it has protons in its nucleus. A negative ion, called an 'anion' (pronounced '
an-eye-en'), is an atom that has one or more electrons forcibly added.
Cations, Anions, Cathodes and Anodes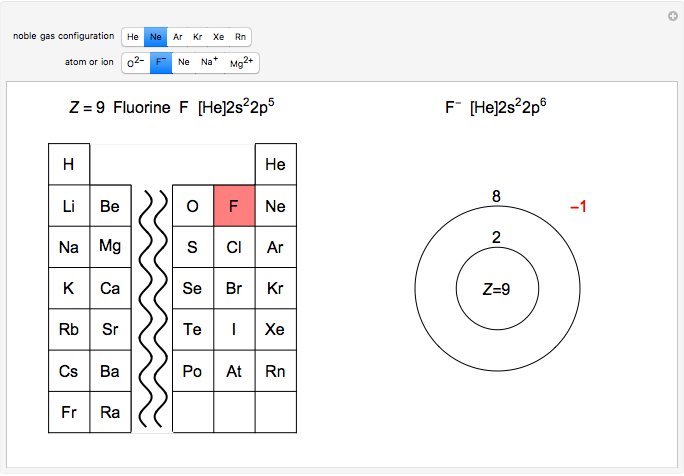
Positive Ionizer
Although one might think cations are in cathodes and anions are in anodes, the opposite is true. When the terms were coined, the concept was that positive cations were attracted to the negative cathode, and negative anions were attracted to the positive anode.
Batteries Contain Positive and Negative Ions In a battery, there are positive ions on one side and negative ions on the other. When a conductor is placed in between to complete the circuit, the electrons flow from the negative ions to the positive side where they join the positive ions. See ion deposition.
Copyright © 1981-2019 by The Computer Language Company Inc. All Rights reserved. THIS DEFINITION IS FOR PERSONAL USE ONLY. All other reproduction is strictly prohibited without permission from the publisher.
Want to thank TFD for its existence? Tell a friend about us, add a link to this page, or visit the webmaster's page for free fun content.
Positive Ions
Link to this page:
Positive Ion Mgo
Positive Ion Air Purifier




